Diamond and graphite are the two most common allotropes of carbon comprising infinite-network solids. In diamond, the carbon atoms are sp3 hybridized and joined by four strong covalent bonds each 0.154 nm long, and joined to four other carbon atoms pointing towards the corners of a regular tetrahedron. Graphite is a layered structure with three 0.1415 nm-long strong bonds within the layer that are sp2 hybridized with one electron able to take on a dual role, forming co-planar and interplanar bonding. These distributions are termed πand σ respectively. The layers are themselves weakly bonded by what can be described as van der Waals forces, which enable the layers to slide over one another. In 1985, the fullerenes, a new allotropic form of carbon, were discovered, comprising both sp2 and sp3 hybridization and are true carbon molecules e.g., C60.
The relationship between the allotropes of carbon is shown in figure 2.1 bellow:
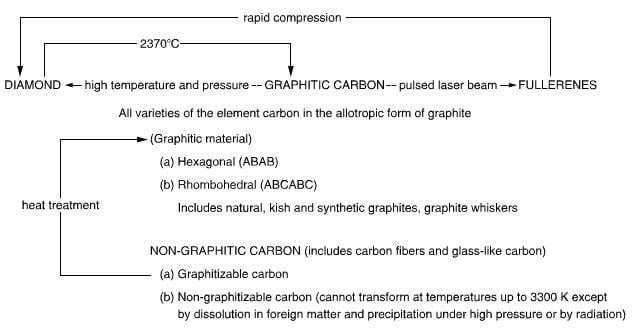
the allotropes of carbon